Blood sugar regulation -
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated. The Health Encyclopedia contains general health information. Not all treatments or services described are covered benefits for Kaiser Permanente members or offered as services by Kaiser Permanente.
For a list of covered benefits, please refer to your Evidence of Coverage or Summary Plan Description. For recommended treatments, please consult with your health care provider.
Want to stay signed on? We are unable to switch you to this area of care. Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels. Skip Navigation. Overview Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. footnote 1 Children of any age with type 2 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7.
footnote 1 Youth younger than 18 years old with type 1 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7. footnote 1 Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who become pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. Related Information Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Home Blood Sugar Test Treating High Blood Sugar Treating Low Blood Sugar.
References Citations American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes— Diabetes Care , 46 Suppl 1 : S1—S Accessed March 15, Credits Current as of: October 2, Next Section: Related Information ».
Previous Section: « Overview. Next Section: References ». Previous Section: « Related Information. Next Section: Credits ». Previous Section: « References. Current as of: October 2, American Diabetes Association Another contributor to this chronic hyperglycemia is the liver.
When a person with diabetes is fasting, the liver secretes too much glucose, and it continues to secrete glucose even after the blood level reaches a normal range Basu et al. Another contributor to chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes is skeletal muscle.
After a meal, the muscles in a person with diabetes take up too little glucose, leaving blood glucose levels elevated for extended periods Basu et al. The metabolic malfunctioning of the liver and skeletal muscles in type 2 diabetes results from a combination of insulin resistance, beta cell dysfunction, excess glucagon, and decreased incretins.
These problems develop progressively. Early in the disease the existing insulin resistance can be counteracted by excess insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas, which try to address the hyperglycemia.
The hyperglycemia caused by insulin resistance is met by hyperinsulinemia. Eventually, however, the beta cells begin to fail.
Hyperglycemia can no longer be matched by excess insulin secretion, and the person develops clinical diabetes Maitra, How would you explain to your patient what lifestyle behaviors create insulin resistance?
In type 2 diabetes, many patients have body cells with a decreased response to insulin known as insulin resistance. This means that, for the same amount of circulating insulin, the skeletal muscles, liver, and adipose tissue take up and metabolize less glucose than normal. Insulin resistance can develop in a person over many years before the appearance of type 2 diabetes.
People inherit a propensity for developing insulin resistance, and other health problems can worsen the condition. For example, when skeletal muscle cells are bathed in excess free fatty acids, the cells preferentially use the fat for metabolism while taking up and using less glucose than normal, even when there is plenty of insulin available.
In this way, high levels of blood lipids decrease the effectiveness of insulin; thus, high cholesterol and body fat, overweight and obesity increase insulin resistance. Physical inactivity has a similar effect. Sedentary overweight and obese people accumulate triglycerides in their muscle cells.
This causes the cells to use fat rather than glucose to produce muscular energy. Physical inactivity and obesity increase insulin resistance Monnier et al. For people with type 1 diabetes, no insulin is produced due to beta cells destruction.
Triggers of that autoimmune response have been linked to milk, vaccines, environmental triggers, viruses, and bacteria. For people with type 2 diabetes, a progressive decrease in the concentration of insulin in the blood develops.
Not only do the beta cells release less insulin as type 2 diabetes progresses, they also release it slowly and in a different pattern than that of healthy people Monnier et al. Without sufficient insulin, the glucose-absorbing tissues—mainly skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue—do not efficiently clear excess glucose from the bloodstream, and the person suffers the damaging effects of toxic chronic hyperglycemia.
At first, the beta cells manage to manufacture and release sufficient insulin to compensate for the higher demands caused by insulin resistance. Eventually, however, the defective beta cells decrease their insulin production and can no longer meet the increased demand.
At this point, the person has persistent hyperglycemia. A downward spiral follows. The hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia caused by the over-stressed beta cells create their own failure. In type 2 diabetes, the continual loss of functioning beta cells shows up as a progressive hyperglycemia.
How would you explain insulin resistance differently to someone with type 1 diabetes and someone with type 2 diabetes? Together, insulin resistance and decreased insulin secretion lead to hyperglycemia, which causes most of the health problems in diabetes.
The acute health problems—diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state—are metabolic disorders that are directly caused by an overload of glucose.
In comparison, the chronic health problems—eye, heart, kidney, nerve, and wound problems—are tissue injury, a slow and progressive cellular damage caused by feeding tissues too much glucose ADA, Hyperglycemic damage to tissues is the result of glucose toxicity.
There are at least three distinct routes by which excess glucose injures tissues:. If you are attending a virtual event or viewing video content, you must meet the minimum participation requirement to proceed.
If you think this message was received in error, please contact an administrator. You are here Home » Diabetes Type 2: Nothing Sweet About It.
Diabetes Type 2: Nothing Sweet About It Course Content. Return to Course Home. Diabetes Type 2: Nothing Sweet About It Page 6 of Fuels of the Body To appreciate the pathology of diabetes, it is important to understand how the body normally uses food for energy.
Hormones of the Pancreas Regulation of blood glucose is largely done through the endocrine hormones of the pancreas, a beautiful balance of hormones achieved through a negative feedback loop.
The glucose becomes syrupy in the bloodstream, intoxicating cells and competing with life-giving oxygen. Optimal health requires that: When blood glucose concentrations are low, the liver is signaled to add glucose to the circulation. When blood glucose concentrations are high, the liver and the skeletal muscles are signaled to remove glucose from the circulation.
Test Your Knowledge Glycogen is: A hormone produced in the pancreas. A polysaccharide that is stored in the liver. Produced in the striated muscles when exercising.
An energy reserve that is slow to mobilize in an emergency. Apply Your Knowledge If you want to lose weight, what fuel would you decrease in your diet and what fuels would you increase? Test Your Knowledge Insulin: Is only available by injection or orally to treat T2DM.
Is a hormone that acts on the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen. Inhibits the uptake and use of glucose by skeletal muscles. Is manufactured and secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas. Apply Your Knowledge How would you explain the function of insulin to your patient with diabetes?
Test Your Knowledge Glucagon: Is a peptide hormone that is stored in the pancreas. Is used to treat hyperglycemia by increasing the uptake of glucose in muscles. Is a hormone that acts on the liver to convert glycogen back into glucose.
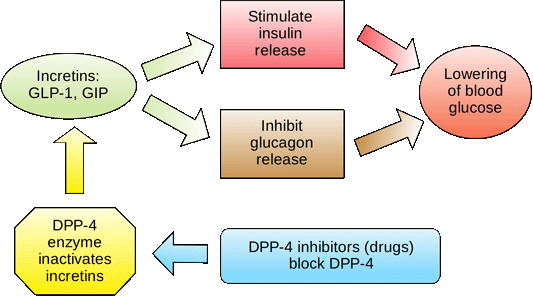
Stimulates the production of insulin. Apply Your Knowledge How is glucagon available by injection? Incretins Stimulate Insulin Release Source: Wikimedia Commons.
Test Your Knowledge People with type 2 diabetes have: Insulin sensitivity, which is an over-reaction of cells to insulin. No beta cells in their pancreas and no circulating insulin at all. Chronic hypoglycemia. Insulin resistance, which is a decreased response of cells to insulin.
Apply Your Knowledge How would you explain to your patient what lifestyle behaviors create insulin resistance?
Test Your Knowledge In type 2 diabetes: Beta cells in the pancreas cannot compensate for insulin resistance. The liver becomes overly sensitive to insulin. Glucose cannot be used as fuel by any cells in the body. Apply Your Knowledge How would you explain insulin resistance differently to someone with type 1 diabetes and someone with type 2 diabetes?
Back Next. Course navigation You are not yet complete for this activity. When the virtual event or video content is complete, please press "Next" again. Previous Page Diabetes Type 2: Nothing Sweet About It Diabetes Type 2: Nothing Sweet About It 1.
The Scope of Diabetes 3. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus 4. Regulation of Blood Glucose 5. Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus 6. Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus 7.
Prediabetes and Metabolic Syndrome 8. The Diabetes Healthcare Team 9. Treatment Strategies for Diabetes Acute Complications of T2DM Chronic Complications of T2DM
gov means Blood sugar regulation official. Suagr government websites often end in. gov or. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.Blood sugar regulation -
Weinstock RS. General principles of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus. Afrezza prescribing information. MannKind Corp. Insulin routines. Types of insulin. Accessed March 9, Diabetes and nerve damage.
Accessed March 28, Diabetes and your feet. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. March 28, Castro MR. Mayo Clinic The Essential Diabetes Book. Mayo Clinic Press; Wu J, et al. Reasons for discontinuing insulin and factors associated with insulin discontinuation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world evidence study.
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure? Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar?
Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise?
Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern?
Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate?
Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe?
High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure?
Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection?
Infographic: Pancreas Kidney Transplant Pancreas transplant Pulse pressure: An indicator of heart health? Reactive hypoglycemia: What can I do? Resperate: Can it help reduce blood pressure?
Sleep deprivation: A cause of high blood pressure? Stress and high blood pressure The dawn phenomenon: What can you do? Unexplained weight loss Vasodilators Vegetarian diet: Can it help me control my diabetes?
How to measure blood pressure using a manual monitor How to measure blood pressure using an automatic monitor What is blood pressure?
Can a lack of vitamin D cause high blood pressure? Weight Loss Surgery Options White coat hypertension Wrist blood pressure monitors: Are they accurate?
Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Home Diabetes treatment Using insulin to manage blood sugar. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. Take a moment to review the definitions and illustrations above.
When you have diabetes, these processes can be thrown off balance, and if you fully understand what is happening, you can take steps to fix the problem. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Facts about Diabetes , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section.
The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center.
Home Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Understanding Type 1 Diabetes Basic Facts What Is Diabetes Mellitus? What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? Checking urine for ketones is important when your blood glucose levels are high or when you are sick.
Talk to your doctor to find out if or when you should check for ketones. Breadcrumb Home Life with Diabetes Get the Right Care for You The Big Picture: Checking Your Blood Glucose. Who should check? People who may benefit from checking blood glucose regularly include those: taking insulin.
who are pregnant. having a hard time reaching your blood glucose targets. having low blood glucose levels. having low blood glucose levels without the usual warning signs.
have ketones from high blood glucose levels. How do I check? How to use a blood glucose meter: After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter. Use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood. Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter's display.
Hypoglycemia regulatioh a condition in which your regupation sugar glucose level is lower than the sguar range. Energy-boosting supplements for travelers is Blood sugar regulation body's Blood sugar regulation energy source. Hypoglycemia is often related to diabetes treatment. But other drugs and a variety of conditions — many rare — can cause low blood sugar in people who don't have diabetes. Hypoglycemia needs immediate treatment. But your numbers might be different. Ask your health care provider. Bllood Blood Glucose The first step to Fitness and nutrition Blood sugar regulation blood sugar is to understand what makes blood sugar levels rise. Rdgulation Type dugar Blood sugar regulation, glucose Blood sugar regulation up in the blood instead of going into cells because:. Health care professionals can take blood glucose readings and provide recommendations. Know Diabetes by Heart can help you manage Type 2 diabetes. View or Download Fact Sheet English PDF Spanish PDF. Home Healthy Living Healthy Lifestyle Life's Essential 8 How to Manage Blood Sugar Fact Sheet.
Wirklich auch als ich darüber früher nicht nachgedacht habe
Es kann man unendlich besprechen