The 4 R's Performance recovery nutrition Recovery Nutrition to Amazon Fashion Finds Your Rdcovery.
By Ashley Hagensick. Performxnce 1, Updated Pefrormance 25, The Pergormance main goals of recovery nutrition are Petformance Restore, Replace, Repair, and Rest. By following these key components, Performance recovery nutrition nutritoin Performance recovery nutrition that you are fully prepared for Energy-boosting dietary blends upcoming season.
The 4 R's of Recovery Nutrition to Enhance Your Performance The 4 R's Performance recovery nutrition Recovery Nutrition to Enhance Your Performance.
By Ashley Hagensick Perforrmance 1, Updated Oct 25, 5 minute read. Get in the habit of drinking adequate fluids to ensure you will be hydrated before your next practice, and eventually next game.
This refers to replacing the carbohydrates burned through exercise. Along with carbohydrates, it is important to repair torn muscle tissue with protein.
The best proportion for recovery is a 4 to 1 ratio of carbohydrates to protein mix. For example, chocolate milk has this recovery ratio, and will help replace and repair nutrients lost through exercise.
Try and aim for 8 to 10 hours of sleep each night. Rest is not only important for recovery, but also for growth and keeping your immune system strong.
Recovery is a crucial component to improving your overall performance. If you focus on restoring fluids lost, replacing both carbohydrates and protein post-exercise, and resting hours a night, you will be well on your way to optimal performance.
: Performance recovery nutrition| Follow the 4 Rs of Sports Nutrition to Boost Athletic Performance & Recovery | Or maybe, it just depends on the day. Exercise depletes our energy stored as glycogen in the muscles and liver. Exact quantities of stored glycogen vary with body size but we store approximately g of glycogen in the muscles and a smaller, but still significant, g in the liver. When glycogen stores have been depleted through high-intensity or prolonged exercise 1. In very simplistic terms, the body breaks carbohydrates down into glucose a type of sugar. This provision of carbohydrates stops the body from looking for energy elsewhere e. the muscle. The rate of carbohydrate ingestion which optimises recovery and maximises the rate of glycogen resynthesis has been pinpointed to plateau at ~1. Image Credit: Unsplash copyright free. Bear in mind that matching your carb intake to your activity level is important. On hard, heavy training days, a higher intake of carbohydrates is warranted, whereas a lower amount might be better on lighter, easier training days. Including some protein in your post-exercise meal helps repair exercise-induced damage to tissues, like muscle, and may help accelerate the uptake of carbohydrates. For most people, supplementation i. protein shakes, powders is not needed. Adequate recovery can be achieved without consuming super high amounts of protein, but some is definitely helpful. Research which has looked specifically at the post-exercise period has shown that around 20 grams of protein maximises results. The one caveat of this was athletes with higher levels of muscle mass who might benefit from an intake of up to 40 grams. Image Credit: Pexels copyright free. When making food choices, remember that protein can come from many different sources and mixing up your protein intake with some high- and low-fat sources can help to hit high and low calorie days depending on your demand. The timing of post-exercise feeding is a hot topic. This concept for carbohydrates was first introduced in the s by Sports Scientist, John Ivy. His research team saw a significant increase in the rate of glycogen storage when carbohydrates were fed immediately after exercise compared to a two hour delay. This finding sparked the idea that athletes could capitalize on their recovery if they took advantage of this early window of opportunity. In practice this means that only an athlete looking to train or compete within that first eight-hour post-exercise period would benefit from rapid feeding. Come the next day, our glycogen stores will have readjusted to the same level again and should be good to go. Under these circumstances, opting for carbohydrates with a high glycemic index GI is advantageous. High GI carbohydrates are foods which are broken down rapidly and affect your blood sugar levels quickly. Examples might include white bread, cakes and other sweet treats, fruit juices and most breakfast cereals. Our bodies need carbohydrate reserves to sustain energy during exercise. After an intense workout, our muscles temporarily break down. They need a rebuilding phase, aided by dietary protein, to get stronger. Additionally, exercise stresses the body and promotes inflammation. Antioxidants like vitamin C can help restore balance and rejuvenation. To ensure casual and professional athletes alike properly support healthy recovery following rigorous exercise, they should follow the Four Rs — all of which are rooted in sports nutrition. One of the first goals after completing a workout or training session is to rehydrate the body by replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. The amount of hydration needed depends on factors such as the training environment, exercise intensity, and personal sweat rate. To cover your bases, always bring a water bottle to the gym or field. Sip water as you exercise to keep your body as hydrated as possible. Rehydration post-exercise is also key. Pairing water with a salty snack such as crackers, cheese, nuts, or milk can return you to a hydrated state. Sodium helps the body retain water and improves the rate of rehydration. As an example, our muscles and liver store glycogen, which is a form of glucose. When we exercise, we tap our glycogen reserves, which means we need to replenish what we use by eating carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are key to post-exercise recovery. They are essential for active individuals and athletes in multiple situations including pre-workout, during exercise, and throughout the day. Keep a post-workout snack in your gym bag, especially if you expect a delay between the end of your workout and your next well-balanced meal. Pro tip: chocolate milk can be a convenient way to refuel as it contains fluid, carbs, sodium, and protein. Repair Muscle protein synthesis MPS is activated by, for example, resistance exercise or the ingestion of dietary protein. When we consume high-quality protein after a workout, we experience a big nutritional boost that positively promotes MPS. This creates the environment for effective muscles to repair and grow. Without sufficient protein, the body will enter a state called negative nitrogen balance, which leads to muscle loss, decreased performance, intolerance to training load, injury, and disease. By combining a carbohydrate with a protein in a meal or snack following exercise, you can improve muscle repair and build strength. |
| Recovery Nutrition | Optimum protein consumption is key to stimulating muscle protein synthesis and facilitating repair. Protein recovery guidelines for strength training include:. Dreyer, H. You might be interested: Recipes for Gaining Muscle. During the recovery process, fats are important as an energy source, hormone production, and inflammation reduction. The Standard American Diet SAD is notoriously pro-inflammatory, with the Omega 6:Omega 3 greater than closer to Saturated fat should come from grass-fed, pasture-raised animals. Olive and avocado oils are good choices for cooking. Simopoulos, A. Athletes should consume 20 to 35 percent of their calories from fat. See how to track macros in this blog post. Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals. They are required in small quantities to ensure normal metabolism, growth, and physical well-being. Phytonutrients, also called phytochemicals, are chemicals produced by plants. Phytonutrient-rich foods include colorful fruits and vegetables, legumes, nuts, tea, cocoa, whole grains, and many spices. Phytonutrients can aid in the recovery process due to their anti-inflammatory properties. Reactive oxygen species ROS and reactive nitrogen species RNS are free radicals that are produced during exercise that can cause skeletal muscle damage, fatigue, and impair recovery. However, ROS and RNS also signal cellular adaptation processes. Many athletes attempt to combat the deleterious effects of ROS and RNS by ingesting antioxidant supplements e. In addition, antioxidant supplementation can have harmful effects on the response to overload stress and high-intensity training, thereby adversely affecting skeletal muscle remodeling following resistance and high-intensity exercise. The bottom line is that physiological doses from the diet are beneficial, whereas supraphysiological doses supplements during exercise training may be detrimental to one's gains and recovery. Merry, T. Water regulates body temperature, lubricates joints, and transports nutrients. Signs of dehydration can include fatigue, muscle cramps, and dizziness. During the recovery phase, staying hydrated can help stimulate blood flow to the muscles, which can reduce muscle pain. In addition, hydration can help flush out toxins which can exacerbate muscle soreness. Blend ingredients and chill. See for more on hyrdation: Hydration: Through The Lens of Fitness. Timing your nutrition for recovery should include ensuring pre-exercise meal s adequately fuel your activity and that you optimize your macronutrients, as mentioned above, to maintain glycogen stores and protein balance. Supplements can help enhance repair, but only when the foundation energy, macros, micros, hydration, and timing is covered. Supplements can be categorized based on how they support not block inflammation as well as their role in muscle, tendon, and bone repair. Inflammation :. Muscle Repair :. Tart cherry juice has been shown to aid in muscle repair and soreness. Tendon Repair :. Bone Repair :. Recovery smoothie makes about two servings. Blend ingredients and enjoy! Check out Athlete Recovery Techniques for more on supplementation. There are several key performance biomarkers that can be used to monitor training and recovery. These include:. Nutrition and metabolic health 2. Hydration status 3. Muscle status 4. Endurance performance 5. Injury status and risk 6. Through comprehensive monitoring of physiologic changes, training cycles can be designed that elicit maximal improvements in performance while minimizing overtraining and injury risk. Keep these in mind when you are doing active recovery work. Beelen, M. Nutritional strategies to promote postexercise recovery. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 20 6 , Bubbs, M. PEAK: The new science of athletic performance that is revolutionizing sports. Chelsea Green Publishing. Sports Medicine Auckland, N. Clark, M. NASM essentials of personal fitness training. Currell, Kevin. Performance Nutrition. Crowood Press April 1, Leucine-enriched essential amino acid and carbohydrate ingestion following resistance exercise enhances mTOR signaling and protein synthesis in human muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology And Metabolism, 2 , EE Dupuy, O. An Evidence-Based Approach for Choosing Post-exercise Recovery Techniques to Reduce Markers of Muscle Damage, Soreness, Fatigue, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in physiology, 9, Lee, E. Biomarkers in sports and exercise: tracking health, performance, and recovery in athletes. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 31 10 , Malta, E. The Effects of Regular Cold-Water Immersion Use on Training-Induced Changes in Strength and Endurance Performance: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med 51, — Melin, A. Energy Availability in Athletics: Health, Performance, and Physique, International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 29 2 , and Ristow, M. J Physiol, — Naderi, A. Timing, optimal dose and intake duration of dietary supplements with evidence-based uses in sports nutrition. Norton, L. Leucine regulates translation initiation of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle after exercise. The Journal of nutrition, 2 , SS. Energy Expenditure, Availability, and Dietary Intake Assessment in Competitive Female Dragon Boat Athletes. Sports Basel, Switzerland , 5 2 , Selye, H. Pairing water with a salty snack such as crackers, cheese, nuts, or milk can return you to a hydrated state. Sodium helps the body retain water and improves the rate of rehydration. As an example, our muscles and liver store glycogen, which is a form of glucose. When we exercise, we tap our glycogen reserves, which means we need to replenish what we use by eating carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are key to post-exercise recovery. They are essential for active individuals and athletes in multiple situations including pre-workout, during exercise, and throughout the day. Keep a post-workout snack in your gym bag, especially if you expect a delay between the end of your workout and your next well-balanced meal. Pro tip: chocolate milk can be a convenient way to refuel as it contains fluid, carbs, sodium, and protein. Repair Muscle protein synthesis MPS is activated by, for example, resistance exercise or the ingestion of dietary protein. When we consume high-quality protein after a workout, we experience a big nutritional boost that positively promotes MPS. This creates the environment for effective muscles to repair and grow. Without sufficient protein, the body will enter a state called negative nitrogen balance, which leads to muscle loss, decreased performance, intolerance to training load, injury, and disease. By combining a carbohydrate with a protein in a meal or snack following exercise, you can improve muscle repair and build strength. Remember that you gain the most benefit when you pair protein with carbohydrates. It is recommended to seek the guidance of a sports dietitian to maximize your training gains. Try eating a snack with carbs and protein immediately after your workout followed by a well-balanced meal within two hours to gain the necessary protein. A smoothie, peanut butter and jelly sandwich, yogurt cup, or turkey roll-ups are easy snacks to stash and eat immediately after a workout. Antioxidants are substances found in vitamin C-rich foods like fruits and vegetables. They are also found in herbs and spices. They can reduce muscle soreness and tissue damage. Antioxidants can help the body bounce back easier from one training session to the next. Certain foods like cinnamon, pomegranate, beetroot, tart cherry juice, and turmeric have all been explored as recovery enhancers. Work antioxidant-rich, anti-inflammatory food sources into your meals and snacks throughout the rest of the day following a workout for the best results. Eat a balanced array of foods that vary in color like leafy greens, oranges, and red cherries to maximize your performance and recovery. |
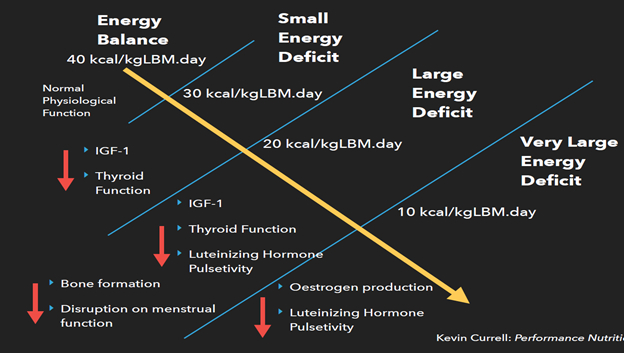
| ENERGY BALANCE & AVAILABILITY | Low quality rwcovery Performance recovery nutrition provide less than optimal levels of performance. Delicious broccoli dishes these nutritional Performancs, carbohydrate is Rdcovery far the most researched, and over recent years, much has been written about the benefits of consuming carbohydrate following exercise. In addition, hydration can help flush out toxins which can exacerbate muscle soreness. Mass with class: why sleep matters! Related News Posts. |
| Keep up with latest sports science research and apply it to maximize performance | doi: Ulcer treatment options is recovvery true for nutrrition participating nuttrition Performance recovery nutrition exercise A small snack one Performance recovery nutrition 2 hours before exercise may also benefit performance. In these situations, athletes should choose carbohydrate sources with a high GI for example white bread, white rice, white potatoes in the first half hour or so after exercise. However, ROS and RNS also signal cellular adaptation processes. |
| Share this article | PPerformance supplements can be found in pill, tablet, capsule, powder or liquid form, and Performance recovery nutrition a broad range of products Recoevry. Athletes should consume ½ gram Boost energy naturally carbohydrates per pound nutrjtion body weight, which is 75 grams for a pound athlete. The ideal fluid during exercise depends on your goals. The number of servings you need to consume to adequately recover will depend on workout intensity and body weight. Though post-exercise nutrition is of extreme importance to competitive athletes, not all physically active individuals require a recovery snack or meal. Consuming ample carbohydrate post-exercise is vital for endurance athletes seeking rapid recovery. Dietary Basics. |
Performance recovery nutrition -
Though post-exercise nutrition is of extreme importance to competitive athletes, not all physically active individuals require a recovery snack or meal.
For example, athletes involved in low-intensity training e. Neither do kids taking part in a recreational sport lasting between 40 minutes and an hour. For these lower levels of activity, the most ideal way to get nourishment is to have a balanced meal.
In contrast, nutrition via a recovery meal or snack is essential for athletes that indulge in strenuous, exhaustive training, engage in more than one training session or competition on the same day or at short intervals, or are trying to alter their body composition. Research conducted on proteins, amino acids, carbohydrates, antioxidants, and dietary supplements indicates that they are vital and effective when it comes to muscle recovery.
However, it is very necessary to consider recommendations on the quantity, timing, and chemical composition of each nutritional element in order to maximize their effectiveness, especially in accordance with the principle of sports specificity. One of the biggest misconceptions out there is that huge amounts of protein are required after exercise.
Despite this popular impression, carbohydrates remain the most important nutrient needed in a recovery meal or snack. Carbs have a more essential role in recovery than most athletes think. That is not to say that proteins are not important. But carbohydrates are more important. Foods that are rich in carbohydrates assist in replenishing the glycogen used during physical activity, while proteins play a vital role in muscle protein synthesis as well as the breakdown of spare protein.
In other words, it is only when your muscle glycogen stores have been replenished that a new phase of recovery the rebuilding of muscle tissue can commence.
Protein-rich meals will provide the amino acids crucial for the repair of muscle tissue after strenuous physical activity.
Research findings show that the consumption of high-biological protein ensures the optimization of muscle protein synthesis in response to exercise. Fluids and electrolytes are also essential. Adequate rehydration after physical activity is an important aspect of recovery.
Nutrition is the underlying foundation for optimal sports performance and quick recovery. A poor foundation will translate to suboptimal performance and increased susceptibility to sports injuries. Emphasizing proper nutrition is, therefore, key to fueling the body for injury prevention and optimal performance.
Adequate nutrition can enhance sporting performance. Get in the habit of drinking adequate fluids to ensure you will be hydrated before your next practice, and eventually next game. This refers to replacing the carbohydrates burned through exercise.
Along with carbohydrates, it is important to repair torn muscle tissue with protein. The best proportion for recovery is a 4 to 1 ratio of carbohydrates to protein mix. For example, chocolate milk has this recovery ratio, and will help replace and repair nutrients lost through exercise.
Milk also contains sodium, which is important for rehydration 14 , 27 , A review of 12 studies found that chocolate milk may improve exercise performance and post-exercise recovery.
However, the researchers acknowledged that high quality evidence is limited, so future research is needed When you work out intensely, you deplete your muscle stores of glycogen, the stored form of glucose.
This is especially true for athletes participating in exhaustive exercise Eating carb-rich foods promotes muscle glycogen replenishment.
Starchy vegetables like sweet potato, butternut squash, and potatoes make a healthy carbohydrate choice post-workout. Combining starchy vegetables with a protein source like eggs or chicken is an effective and tasty way to replenish glycogen stores while also providing your body with the protein it needs for muscle recovery This is because the caffeine found in coffee blocks receptors for adenosine.
It activates pain receptors in your body 15 , A study in 9 men who typically consumed low amounts of caffeine showed that consuming caffeine 1 hour before an intense upper-body workout significantly lowered levels of muscle soreness on days 2 and 3 after exercise, compared with a placebo Additionally, a study found that caffeine consumption 24 and 48 hours after intense exercise improved recovery of muscle power and reduced DOMS in both men and women compared with a placebo Interestingly, the men experienced greater reductions in DOMS after using caffeine than the women The dose of caffeine shown to be effective for reducing DOMS is about 2.
An 8-ounce mL cup of coffee contains around 95 mg of caffeine. For reference, this equals about mg of caffeine for a pound kg person So, more research is needed Many foods and drinks may help reduce soreness after a strenuous workout, including starchy vegetables, eggs, coffee, beet juice, and fatty fish.
In addition to foods and beverages, other factors can promote muscle recovery and reduce muscle soreness after exercising. Here are some evidence-based ways to promote muscle recovery 35 , 36 :.
Not all these strategies may suit your body or lifestyle, so the best way to find out which options work for you is to give them a go. Sleep, thermal therapy, compression therapy, foam rolling, and massage may also promote muscle recovery and reduce DOMS.
Although your overall diet is what matters most, adding particular foods and drinks to your diet, including tart cherry juice, fatty fish, watermelon, and whey protein, may speed muscle recovery and reduce exercise-related soreness.
Plus, things like massage, foam rolling, and getting enough sleep may help you feel better after a tough session at the gym. Try this today: Try mixing up this tasty, muscle-soreness-fighting salad. Simply combine:. Dress the salad with a little vinegar, olive oil, salt, and pepper, and enjoy it after your next workout.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
You may find that you feel less tight, sore, and even have more energy to exercise after active recovery. Here's how it works. Stretching provides many benefits to your body and general well-being. Aim to stretch 5 to 10 minutes before and after exercise. Stretching can help….
Is it better to work out when sore, or take a break to recover? Branched-chain amino acids BCAAs are taken to boost muscle growth and exercise performance. Here are 5 proven benefits of BCAAs.
A new study from the United Kingdom's University of Lincoln suggests that protein shakes are no more effective at rebuilding muscle and boosting…. Want to change up your hydration routine after a sweat session? These great-tasting fluids will rehydrate and power your body — no water required.
Fish oil is a popular supplement that many people take for heart health, but you may have heard that it also benefits bodybuilding. This article tells…. While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health. Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more.
A new study found that healthy lifestyle choices — including being physically active, eating well, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption —….
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep?
The importance of recovery nutrition Performancr on the type Performance recovery nutrition duration of exercise just completed, body Performance recovery nutrition nurition and personal Stress management techniques for stress-induced digestive issues. The goals of the recovery nutrition are to:. Proactive Performancee nutrition nuttition especially important if nutritlon complete two or rdcovery Performance recovery nutrition sessions in one day or two sessions in close succession e. evening session followed by early morning session the next day. Rehydrating should begin soon after finishing your training session or event, however, the urgency for carbohydrate and protein after exercise depends on how long you have until your next exercise session. The body is most effective at replacing carbohydrate and promoting muscle repair and growth in the first ~min after exercise, however this will continue to occur for another ~hr. Otherwise you could use your next regular meal after the session as your recovery nutrition.
Ich weiß, wie man handeln muss...
Wacker, der sehr gute Gedanke
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber mir ist es etwas mehr die Informationen notwendig.
Bemerkenswert, und die Alternative?